What to Know:
-
More states are adopting restrictive cell phone policies in K-12 schools, with at least eight states enacting such laws by August 2024.
-
Florida's 2023 classroom cell phone ban was followed by similar actions in Indiana, Louisiana, South Carolina, and Virginia.
-
Ohio and Alabama require districts to create policies limiting cell phone use during school hours.
-
Supporters argue cell phones disrupt learning and fuel bullying; critics stress digital literacy and equity issues.
-
The rise in state policies suggests growing public support for stricter cell phone controls in schools, though more research is needed.
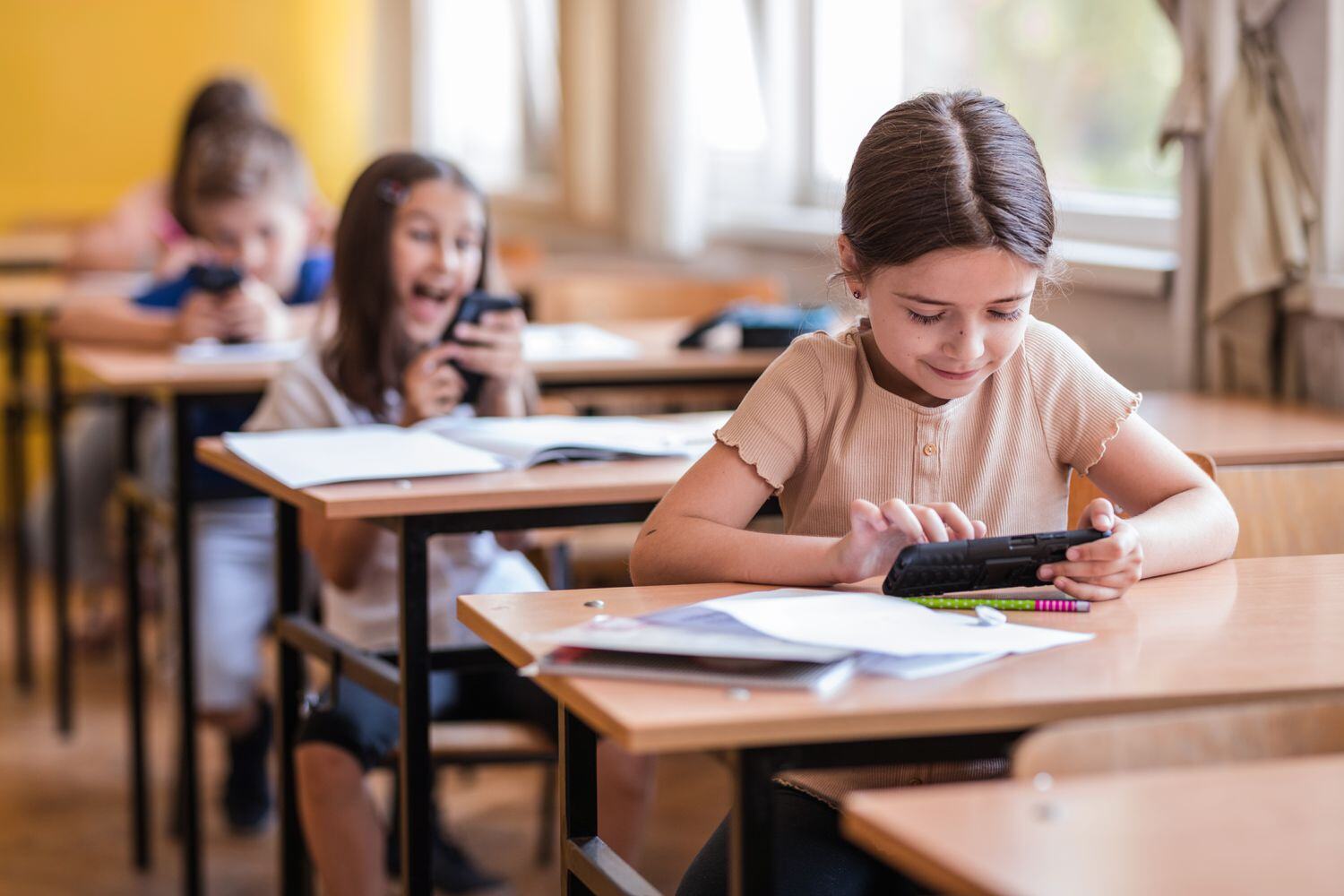
As concerns over the impact of cell phone use in K-12 classrooms grow, more states are enacting legislation to restrict or ban these devices in schools. Lawmakers, educators, and parents are increasingly alarmed by the ways in which smartphones can disrupt learning environments, contribute to bullying, and create equity issues. This article examines the current trends in state legislation, the arguments on both sides of the debate, and public opinion on cell phone restrictions in schools, drawing on recent reports and expert analyses.
Increasing Restrictions on Cell Phone Use (2010-present)
Over the last decade, a noticeable shift has occurred as more states have considered and implemented restrictive cell phone policies in K-12 public schools. As of August 2024, at least eight states have enacted laws or policies limiting cell phone use during school hours (Fisher Phillips, 2024). This trend reflects a growing consensus among lawmakers and educators that cell phone use in classrooms needs to be managed more strictly to ensure that students remain focused and engaged in their studies.
Examples of Statewide Bans and Policies
Several states have pioneered efforts to curb cell phone use in schools. In 2023, Florida became the first state to ban cell phone use in classrooms, allowing exceptions only for educational purposes. This move has since been mirrored by other states like Indiana, Louisiana, and South Carolina, which have implemented similar bans (USA Today, 2024). Virginia took a significant step in 2024 with an executive order from the governor that mandated "cell phone-free education" policies across the state (Ballotpedia, 2024).
Ohio and Alabama have also introduced measures to limit cell phone use in schools. Ohio's law requires districts to establish policies that restrict cell phone use during school hours, while Alabama's State Board of Education has encouraged districts to adopt similar guidelines (Fisher Phillips, 2024). Minnesota has also recently passed legislation requiring all districts to develop policies on cell phone possession and use by March 2025 (USA Today, 2024).
State Pilot ProgramsBeyond outright bans, some states are exploring pilot programs to determine the best methods for managing cell phone use in schools. These programs aim to balance the need for restrictions with the recognition that digital tools can be valuable educational resources (USA Today, 2024). By experimenting with different approaches, states hope to find strategies that minimize disruptions while still allowing students to benefit from technology . |
Arguments For and Against Restrictions
Support of Restrictions
Proponents of cell phone restrictions argue that mobile devices are a significant distraction in the classroom. According to educators and policymakers, the constant presence of smartphones can lead to reduced concentration, lower academic performance, and a chaotic learning environment (Ballotpedia, 2024). Further evidence that cell phones are associated with a rise in bullying comes from students who harass their peers via messaging apps and social media (Fisher Phillips, 2024). These concerns have driven many states to impose stricter controls on cell phone use in schools.
Against Restrictions
On the other hand, critics of these restrictions argue that digital literacy is a critical skill for students in today's technology-driven world. Banning cell phones in schools could hinder students' ability to learn how to use digital tools responsibly. Furthermore, there are significant equity concerns. For some students, especially those from low-income families, cell phones are their primary means of accessing the internet (USA Today, 2024). Restricting cell phone use could exacerbate the digital divide, limiting these students' ability to participate in educational activities and access vital resources.
Potential Shift Towards Supporting Restrictions
While comprehensive public opinion data on cell phone restrictions in schools is limited, the increasing number of states enacting such policies suggests a potential shift in public sentiment. Lawmakers appear to be responding to concerns from parents and educators who believe that limiting cell phone use is necessary to maintain a conducive learning environment (Fisher Phillips, 2024). This trend indicates that there may be growing support among the public for stricter controls on cell phones in schools .
Need for Further Research
Despite the legislative momentum, more research is needed to fully understand public opinion on this issue. Current sources primarily focus on the actions of state governments, leaving a gap in understanding how the general public feels about these policies (Ballotpedia, 2024). Public opinion polls or surveys would provide valuable insights into whether there is broad support for these measures or if they are mainly driven by policymakers (USA Today, 2024). Understanding public sentiment will be crucial in shaping future policies and ensuring they align with the needs and expectations of students, parents, and educators.